Back to employers
Automotive & Mechanics
Australia’s automotive and mechanics industry is massive and holds tonnes of exciting opportunities for car lovers, DIY enthusiasts, and anyone who doesn’t want to spend their 9-5 stuck at a desk! The best part? There are so many different automotive careers to choose from; even the pickiest job-hunter is bound to find something they love.
If we’ve piqued your interest, and we know that we have, it might just be time to dive deeper into the automotive industry in Australia. Our automotive and mechanics industry page is the perfect resource for anyone wanting to launch a rewarding auto career. So, what are you waiting for? Dive in and land your dream job today!
Whether you’re a car and vehicle enthusiast, or simply feel drawn to hands-on work and technology, an automotive career can be a great pathway that helps you follow your passion (while earning a comfortable wage, too).
However, when most people think of the automotive and mechanics industry, the first thing that comes to mind is working as a car mechanic. While this is a super fulfilling (and exciting) role, it definitely isn’t your only option if you’re considering an automotive career. In fact, when you really think about it, automotives, vehicles and general transport are crucial for most, if not all, industries to function effectively. This means that there are a lot of automotive and mechanics roles to explore within multiple industries!
Some of the lesser-known activities you might end up doing as part of your automotive career include:
- Retailing (A.K.A. selling) vehicles, parts and tools.
- Parts manufacturing.
- Mechanical and electrical engineering.
- Executing repairs and maintenance for cars, trucks and heavy goods vehicles.
- Repairing and servicing bicycles, outdoor power equipment, marine vessels and motorcycles.
- Non-car manufacturing.
See? There’s a lot more to the automotive and mechanics industry than meets the eye!

Automotive and Mechanics Roles: Create the Career of a Lifetime
As the automotive and mechanics industry continues to expand and grow with exciting innovations like self-driving cars and electric vehicles, more opportunities are entering the market. In other words, new automotive careers are popping up all the time!
Just think about all the work it takes to ensure that electric vehicles keep running: it takes many helping hands, like those of EV technicians, battery engineers, and charging station installers. These auto careers are all relatively new, too (the first mass produced hybrid car didn’t even come out until 1997), so it’s exciting to think about where future advances can take the automotive and mechanics industry in the future. Especially when we consider all of the potential automotive careers that may be invented as a result.
An extra benefit of choosing to work in the automotive and mechanics industry is that you’ll be able to choose from multiple different career pathways! Depending on the type of role you’d ultimately like to land, you could choose from traineeships and apprenticeships, degree pathways, and direct employment. It’s all about what works best for you!
What You Could Do
While the classic car mechanic profession seems to be the face of the automotive and mechanics industry, there are so many other auto careers to explore! To help you find your perfect fit, we’ve put together a list of exciting potential roles; and who knows? You might just discover your dream job!
Some of the top jobs you could explore in the automotive and mechanics industry are:

Driving Instructor
Driving Instructor Average Salary: $80,000 – $90,000
Driving Instructor Role Description: Combine a love of cars with a love of teaching by becoming a driving instructor! You’ll support a range of individuals to get behind the wheel and gain the confidence they need to pass their driving test. It can be a rewarding role but also one that requires lots of patience, exceptional communication skills, and the ability to appropriately manage others.
If spending your days in a workshop isn’t quite your speed and you love a good road trip, this automotive career could just be your perfect fit!
Tire Technician
Tire Technician Average Salary: $100,000 – $120,000
Tire Technician Role Description: Tire technicians service, repair, and replace car tires to ensure an efficient and smooth ride for drivers. They’re knowledgeable about various tire types, and recommended treads for various road or off-road environments. Essentially, they help keep people safe on the roads, that’s why they play such a key part in the automotive and mechanics industry.
In regard to where they work, they could be employed by a tire specialty repair shop or as part of a bigger automotive technician team in a large auto body shop; it’s up to them!
Vehicle Inspector
Vehicle Inspector Average Salary: $85,000 – $100,000
Vehicle Inspector Role Description: If you’re looking for an automotive career that really makes a difference, this one’s for you! Vehicle inspectors are responsible for ensuring vehicles meet safety standards for the industry they’re used within and for general public use.
As someone working in this auto career, you’d spend your days conducting safety checks using a variety of methods, tools and apparatus to get a full understanding of the vehicle you’re working on. Once repairs and maintenance are carried out, vehicle inspectors usually re-conduct their tests to make sure the vehicle really passes quality standards.
Auto Electrician
Auto Electrician Average Salary: $75,000 – $95,000
Auto Electrician Average Salary: In short, auto electricians inspect, repair and maintain anything electrical within a vehicle. This includes the headlights, dashboard warning lights, alarm system, circuit boards and starter motor, too! They use a range of tools and diagnostic equipment to test the different electrical components, determine where faults lie and to decide how to repair them.
As key parts of the auto and mechanics industry, auto electricians might work as sole traders or within auto body shops alongside other mechanics and auto engineers.
Auto Mechanic
Auto Mechanic Average Salary: $75,000 – $90,000
Auto Mechanic Role Description: The auto (or car) mechanic profession is probably what comes to mind first when you think about working in the automotive and mechanics sector. They carry out routine maintenance, diagnostic testing and mechanical repairs on a range of different vehicles and usually work on motorised components, such as engines, drive belts, power steering, brakes and transmissions.
Like other automotive technicians, auto mechanics use a range of tools and diagnostic equipment to help, but with older cars this isn’t always possible, so they need to have excellent auto knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Auto Engineer
Auto Engineer Average Salary: $80,000 – $117,000
Auto Engineer Role Description: In a nutshell, auto engineers research, design and develop technical systems for different vehicles. They utilise innovative technology to improve navigation, warning, control, and fuel systems.
They usually work to continually improve previous systems and focus on what specific drivers need to make their driving experience safer. They also troubleshoot any problems that arise and work on solutions before new ideas, parts, or systems go into production. If you’re looking for an exciting auto career with a high earning potential, this one might be your perfect fit!
One of the best parts about the automotive and mechanics industry is that this list of exciting automotive careers is only just scratching the surface. If you’re passionate about cars but find yourself dreaming of a different pathway, all you need to do is a little research; we guarantee you’ll find the right auto career for you! In fact, we’re willing to bet that the more you explore the sector, the more opportunities you’ll come across.
Insights into the Automotive & Mechanics Industry
When we’re choosing a career, we always want to invest our efforts in a sector that’s future proof. And luckily, if you’re choosing a career in the automotive and mechanics industry, you don’t have to worry! In fact, the automotive and mechanics industry revenue has grown at a CAGR (otherwise known as ‘compound annual growth rate’) of 1.1 % over the past five years and is expected to keep going up!
Hiring Trends
To give you a deeper understanding of just how important automotive careers are to the economy, we’ve put together the following stats:
-
- High Demand: Mechanical engineering roles.
- High Demand: Fabrication engineering roles.
- Moderate Demand: Panel beaters.
- Moderate Demand: Vehicle body builders.
- Moderate Demand: Trimmers.
- Moderate Demand: Painters.
While the automotive and mechanical industry took a dip during COVID-19, thanks to lockdowns, low travel and stay-at-home orders, the industry is again on the up, with a surge of expected growth between now and 2028. Technological upgrades and new product developments also significantly benefit the sector’s growth and create plenty of auto career opportunities!
Graduate Employment
Completing a degree isn’t necessary for many roles within the automotive and mechanics industry unless you want to pursue a career as an engineer. In fact, apprenticeships tend to be a popular route into the industry (and there are plenty of exciting ones on offer). However, it’s still important to research all of your options; knowing what graduate employment looks like can help set your expectations and make decisions about how you want the future of your auto career to look.
However, while you don’t have to earn a university degree (unless you’re going into engineering), it can definitely help! In fact, more than 80% of engineering graduates find employment within six months of graduating; so if you’re looking for job security, having a degree under your belt can be pretty comforting!
Gender Split
While we’re making slow but steady progress, the automotive and mechanics industry is still heavily male-dominated. In fact, despite making up 47.9% of Australia’s workforce, women make up a mere 20% of the auto industry. There is also a large discrepancy in enrolment rates, and only 4.5 percent of enrolments in Certificate III in Light Vehicle Mechanical Technology come from women. However, women enrolments in Certificate II in Automotive Vocational Preparation are slightly better at 13.2.
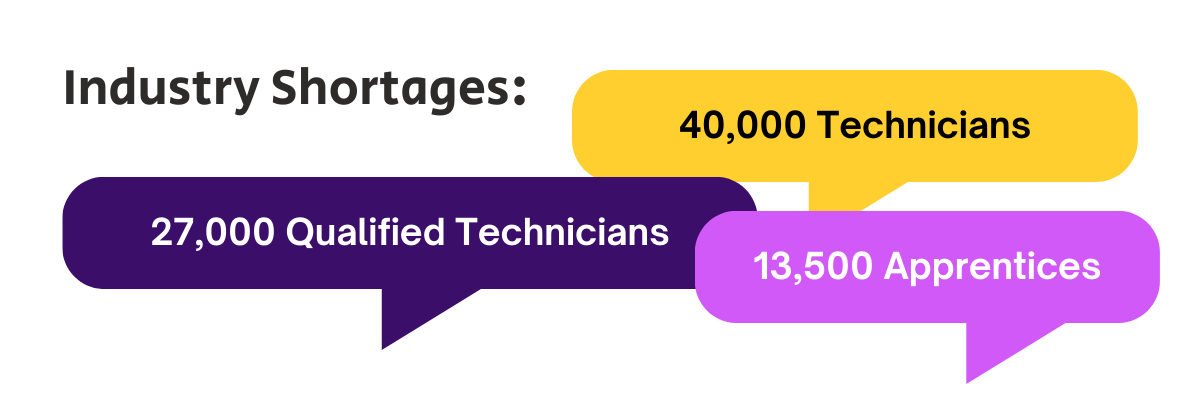
Despite gradual improvements, it’s time to pick up the pace. We’d love to see more women in the automotive and mechanics industry. In fact, they’re needed! According to AAAA’s research, the industry is short of almost 40,000 technicians: 27,000 qualified technicians and 13,500 apprentices, so there are plenty of automotive careers to go around.
At Explore Careers, we’re actively working with employers to help them promote Gender Diverse & Gender Positive workplaces (and many of our employer partners in the automotive and mechanics industry actively encourage applications from women)!

Automotive & Mechanics Salary
A misconception about the automotive and mechanics industry is that it doesn’t pay particularly well. However, according to our research, that couldn’t be further from the truth! If you’re curious about auto careers and their corresponding salaries, keep on reading, because we’re letting the cat out of the bag.
Current surveys in the sector indicate the median salaries for full-time roles in this industry as:
- Car Salesman Average Salary: $46,000 – $56,000 + $43,000 bonus / commission
- Tow Truck Driver: $75,000 – $83,000
- Auto Mechanic Average Salary: $75,000 – $90,000
- Auto Electrician Average Salary: $75,000 – $95,000
- Driving Instructor Average Salary: $80,000 – $90,000
- Auto Engineer Average Salary: $80,000 – $117,000
- Vehicle Inspector Average Salary: $85,000 – $100,000
- Tire Technician Average Salary: $100,000 – $120,000
While these numbers are based on the salaries of real people in the automotive and mechanics industry, it’s important to note that salaries can be pretty varied. So, if you’re starting out in an entry level role, you might want to go in with slightly lower expectations.
Salaries for auto careers (or any careers for that matter!) are also determined by several factors, including:
- The segment of the industry you work within.
- Your job title and seniority.
- The amount of experience you have.
- Any additional qualifications or certifications that give you a specialist skillset
- The company’s budget.

Qualifications and Entry Pathways
Regardless of what your ideal pathway may look like, there’s guaranteed to be an option that fits your preferences in the automotive and mechanics industry. And if you already know university isn’t for you, don’t sweat it! There are plenty of alternative opportunities to choose from. Or alternatively, is completing a university degree a must-do item on your bucket list? That’s cool too; completing a bachelor’s or master’s is a great way to kickstart your automotive career.
Entry pathways for auto careers are super varied and will depend heavily on the type of role you want to get into. You’ll typically need at least your high school education certificate for most roles and learn on the job while you gain industry-relevant qualifications (but if you ask us, that’s a pretty cool way to do things)!
Before we break down all your options, this is what you need to know: nationally recognised training for automotive ad mechanical roles are delivered under two regulatory bodies:
- AUM – Automotive Manufacturing Training Package
- AUR – Automotive Industry Retail, Service and Repair Training Package.
Both programs are fantastic for those wanting to break into the automotive and mechanical industry, however you’ll want to check which one best suits your needs and sets you up for your preferred auto career.
 Degrees for Automotive and Mechanical Careers
Degrees for Automotive and Mechanical Careers
While we always love giving you options, engineering roles in the automotive and mechanical industry will require you to complete a relevant degree program. However, if you didn’t envision yourself committing to tertiary education, don’t worry too much. As you’ll soon see, these degrees are actually pretty cool.
Bachelor of Engineering (Mechanical Engineering)
Time to Complete: 4 years full-time
If you’re hoping to launch an automotive career in engineering, a Bachelor of Engineering, majoring in mechanical engineering, could be the perfect option for you! This degree is based on mechanical engineering, but it can also equip you with specialist knowledge about automotive engineering too.
And don’t forget: more than 80% of engineering graduates find employment within six months of graduating, and that’s a pretty impressive number!
Bachelor of Technology (Motorsports)
Time to Complete: 3 years full-time
This degree is pretty cool, especially if you’re an avid F1 fan looking for an automotive career (in fact, it almost has us going back to university). When studying a Bachelor of Technology and majoring in motorsports, you’ll gain a solid understanding of ‘the design, simulation and fabrication processes, and the management issues associated with production of the complex automotive systems and the components that underpin the motorsport industry.’
This course is perfect for those wanting to break into the automotive and mechanics industry and will have you feeling excited to make your morning class! Plus, you’ll be spending your class time with other motorsports enthusiasts; we consider that a big win!
 Best Places to Study
Best Places to Study
Choosing where to study can feel like a massive, life changing decision. However, when you’re armed with tonnes of research and know exactly what schools teach your potential degree best, the decision becomes a whole lot easier!
Where you choose to study will be dependent on a range of factors, but some top institutions to study subjects related to the automotive and mechanical industry include:
- Australian Trade Training College
- RMIT University
- University of Western Australia
- University of Southern Queensland
- Swinburne University of Technology
- TAFE (Nationwide)
- Queensland University of Technology
Your local TAFE and vocational education providers are also excellent places to reach out to and explore your apprenticeship and vocational qualification avenues with!
 Alternative Automotive and Mechanical Pathways
Alternative Automotive and Mechanical Pathways
Still think that university isn’t quite right for you? You can also pursue tonnes of other exciting careers in the automotive and mechanical sector through opportunities like:
Apprenticeships and Traineeships
Apprenticeships and traineeships are perfect options for auto enthusiasts who want to jump straight into the industry and earn while they learn! These programs give you super valuable hands-on experience, help you build your network of industry pros and allow you to gain industry-specific qualifications alongside your certificate of education.
It’s important to note that apprenticeships and traineeships in the automotive and mechanical industry can vary considerably, so it’s important to figure out which one is right for you. Consider your auto career aspirations, the amount of time you’re willing to invest, and the type of company you want to work with before diving in.
Work Experience
If you’re still at school but want to give your career a head start, consider reaching out to local businesses and asking if you can get some hands-on experience! Not only will this help you develop crucial skills for your auto career, but it’ll also set you up with connections in the automotive and mechanical industry.
You don’t have to dedicate too much time to this either; when you’re first starting out, one day a week is more than enough to get your foot in the door!
TAFE and Vocational Education Pathways
If university, apprenticeships, traineeships and work experience pathways aren’t quite for you, TAFE courses could be the perfect way for you to pursue a career within the automotive and mechanical sector!
Not sure where to start? Here are a few of the qualifications you may want to consider:
Requirements will depend on the type of auto career you want, so make sure you do your research. However, make sure you don’t hold back either! Whatever your circumstances, grades, or preferred way forward, there’s a qualification pathway that will work for you.
Top Skills You’ll Need
Some of the key skills identified to be successful in the industry include:
1. Technical Skills
A solid grasp of vehicle systems, such as engines, transmissions, brakes, and electrical components, can be incredibly helpful when building your automotive career. This expertise helps you execute accurate diagnostics and effective repairs, ensuring vehicles remain reliable and safe on the road! However, you aren’t expected to have this from the get-go; you’ll learn as you work, so don’t stress too much!
2. Problem-Solving Abilities
Mechanics frequently encounter brain-bending issues that require logical thinking and innovative solutions. Strong problem-solving skills allow technicians to identify root causes swiftly which, in turn, reduces vehicle downtime and enhances customer satisfaction! Plus, this skill can be applied to any job, regardless of whether it’s in the automotive and mechanical industry or not.
3. Attention to Detail
Precision is super important in automotive and mechanical work. Taking a very meticulous approach ensures that everything is done right and effectively prevents potential failures. Working on people’s cars is a big responsibility, but if you’re careful and detail-oriented, you’ll thrive in an auto career!
4. Technological Aptitude
As we all know, the automotive and mechanical industry is becoming more and more high-tech. With the integration of advanced technologies in modern vehicles, familiarising yourself with diagnostic tools, software, and electronic systems is pretty important.
5. Communication Skills
There are so many situations that require clear communication in the automotive and mechanical industry. For instance, you’ll need this skill when you talk to clients about vehicle issues, repair timelines, and costs. Additionally, effective collaboration with team members enhances workshop efficiency which is crucial for anyone in an auto career!
6. Physical Dexterity
Careers in the automotive and mechanical industry can involve working in confined spaces and handling various tools; these auto careers are definitely not for the weak of heart! Good hand-eye coordination and physical stamina are super important to perform tasks safely and efficiently.

Where to Learn More
If we’ve piqued your interest in the automotive and mechanical industry, we have even more resources to help you prepare for a rewarding auto career.
You can learn more about different career pathways through professional bodies and organisations advocating for careers in the sector, and some great places to start include:
Pro tip: Each state will also have several professional organisations to help you learn more about the industry, network, and develop your auto career, so keep an eye out for which associations that are local to you!
Finally, if you like our style and want to meet some cool employers in the automotive and mechanical industries, check out the blogs below (and who knows, the featured employers might just end up being your new place of work)!

The Future of Automotive Careers for Apprentices
Get to know our friends at mycar by discovering car-related career pathways and discover how you can land the automotive apprenticeship of your dreams!
Explore

Launch a Career with Toyota, But Not as You Know It
Want to launch an exciting auto career, learn about automotive mechanics and dive into the automotive industry in Australia? Check out our guide today!
Explore





 Degrees for
Degrees for  Best Places to Study
Best Places to Study Alternative
Alternative 





